I've been working with AI ecosystem for the past three years, and I've watched the same frustrating scenario play out countless times.
/blog/email-marketing-strategies-2024. They click… and boom—404 error.Your visitor's trust drops instantly. They bounce. You lose a potential conversion, and worse? You don't even know it happened.
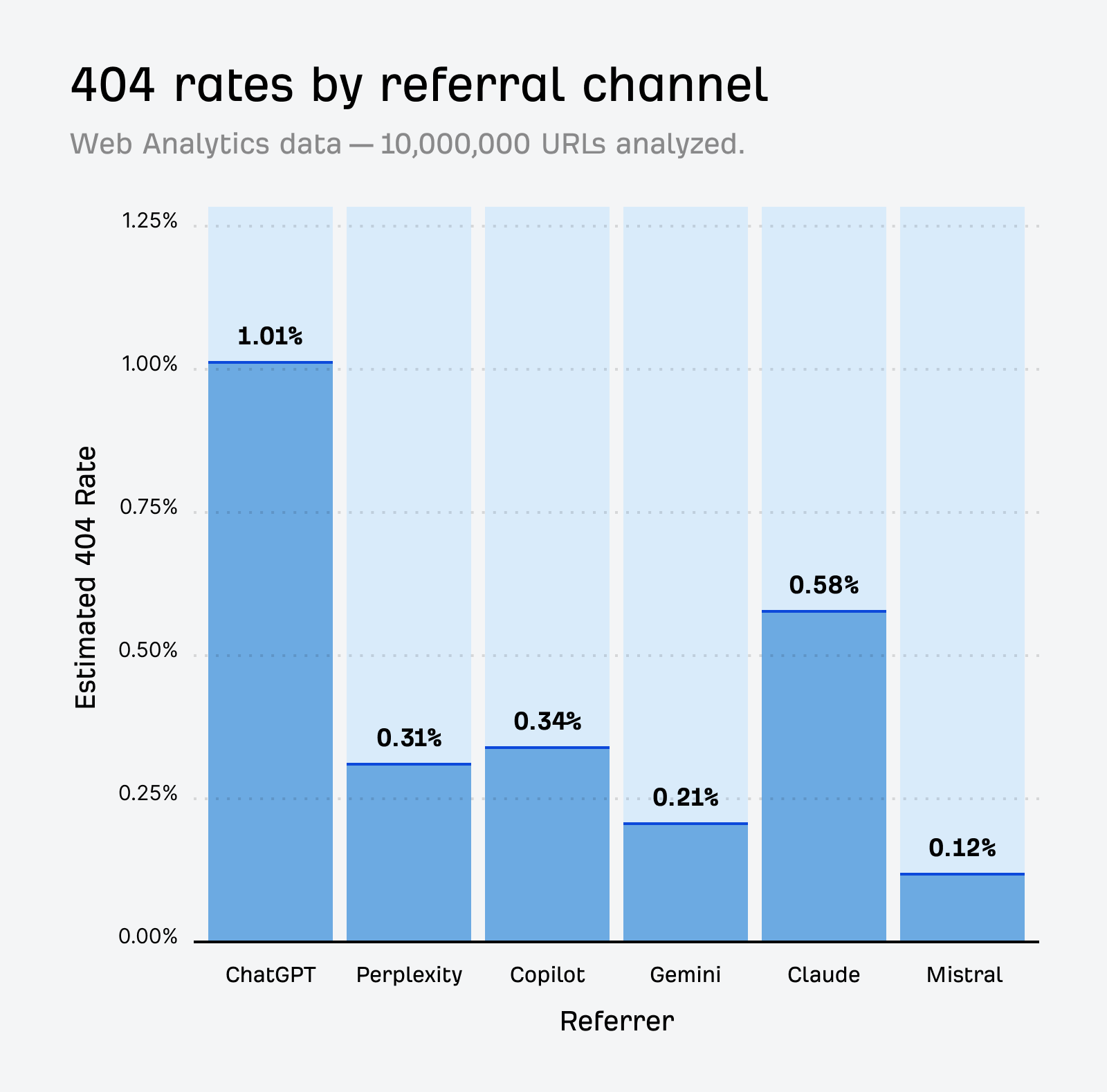
The problem is real—and it's growing. Recent data shows that AI assistants send visitors to 404 pages 2.87x more often than Google Search, with ChatGPT being the greatest offender, with 1.01% of clicked URLs and 2.38% of all cited URLs returning a 404 status. What's even more concerning? Over 70% of users who encounter a 404 error are likely to leave the website if they don't find a quick resolution.

But here's the thing—I've also seen the solution working firsthand. Let me walk you through exactly what these AI-generated 404s are, why they matter more than you think, and two proven ways to recover that lost traffic.
What Are AI-Generated & Hallucinated Links?
Let me clarify the terminology because this confusion trips up a lot of teams…
AI-generated links are any URLs that language models create while responding to user prompts. Think of when someone asks ChatGPT "Where can I find [your company's] guide to email marketing?" The AI might confidently respond with something like "You can find it at yoursite.com/email-marketing-complete-guide."
Hallucinated links are the subset that don't actually exist. They're the ones sending your potential customers to frustrating 404 pages instead of your carefully crafted content.
I've noticed specific patterns in my analytics data. The most common hallucinations include:
- Invented slugs that sound logical:
/blog/internal-link-building-guide/when your actual URL is/resources/link-building-strategy/ - Fake citations to authoritative content: AI references your "comprehensive SEO audit checklist" that never existed
- Date-based assumptions: URLs like
/2024-marketing-trends/when you publish trend content under different naming conventions
The reason this happens comes down to pattern matching without ground truth. LLMs are incredibly good at recognizing URL structures and creating plausible-sounding paths based on your site's existing patterns. But they're essentially educated guesses without verification.
I learned this the hard way when I discovered ChatGPT was confidently linking to /tools/keyword-density-checker/ on a client's site. The tool existed, but it lived at /seo-tools/keyword-analysis/. Close enough to feel intentional, wrong enough to break the user experience.
Why Hallucinated Links Matter More Than You Think

The impact goes beyond simple user frustration. I've tracked three specific areas where these phantom URLs hurt your business:
Trust and brand perception take an immediate hit. When someone specifically seeks out your content through AI assistance and lands on a 404, it feels like your brand made a promise it couldn't keep. They're not just disappointed—they question your competence.
From an SEO and analytics perspective, these broken journeys pollute your data. You're seeing increased bounce rates from visitors who never had a fair chance to engage with your actual content. Plus, search engines may interpret these patterns as poor user experience signals.
Operational costs add up quickly. Your content team starts fielding support tickets about "missing" pages. Developers waste time investigating URLs that were never supposed to exist. Marketing teams lose confidence in AI-assisted content promotion.
I've seen companies spend weeks mapping phantom URLs only to find new ones appearing faster than they can patch them. That's exactly why systematic solutions matter.
Solution 1: Instant Recovery with Fix404.dev (Drop-in Approach)
When I need results today without backend engineering, I developed a free tool with Claude Opus 4.1: Fix404.dev. It's designed specifically for this problem—smart, relevant suggestions on every 404 page with zero infrastructure requirements.
LLMs generate broken links to your domain daily. Fix404 recovers these lost visitors by dynamically suggesting real, relevant content on your 404 pages.
Here's how it functions under the hood:
- Detection and parsing: The moment someone hits a 404, the system analyzes the requested path and extracts meaningful keywords from the slug
- Intelligent search: It queries Google for the best matching pages specifically on your domain
- SERP-style presentation: Suggestions appear with familiar titles and snippets, making the recovery feel natural
- Analytics integration: Every recovered click gets tracked in GA4 with clear attribution (utm_source=fix404-hallucination)
- Privacy-first approach: Searches are anonymized with no user data stored
The implementation couldn't be simpler. Here's what I add to 404 pages:
<!-- Place where you want suggestions to appear -->
<div id="fix404-widget"></div>
<!-- Replace with your actual domain -->
<script src="https://widget.fix404.dev/loader.js"
data-domain="yourdomain.com"></script>I've implemented this across WordPress sites, React applications, and even Shopify stores. The beauty is platform independence—it works wherever you can add HTML.
What to measure once it's live:
- Recovered sessions (404 → suggested link clicks)
- Assisted conversions tagged with utm_source=fix404-hallucination
- 404 bounce rate before vs. after implementation
- Top hallucinated slugs generating the most recovery traffic
In my experience, you'll typically see 15-25% of 404 visitors click through to suggested content, with about 60% of those continuing to browse normally.
The main trade-off is that suggestions rely on live Google search results. If you need custom ranking logic—like prioritizing product pages over blog posts, or boosting newer content—you'll want the control that Solution 2 provides.
Solution 2: Custom RAG-Based Links on Cloudflare (Full Control)
For larger sites or when you need sophisticated ranking logic, I build custom RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems on Cloudflare's edge network. This approach gives you complete control over the suggestion experience while maintaining sub-50ms response times globally.
When to choose this route: You want custom ranking algorithms, need to support multiple domains, require specific business rules (like never suggesting discontinued products), or you're dealing with high traffic volumes where edge performance matters.
Here's the high-level architecture I typically implement:
Content ingestion pipeline: A scheduled job crawls your sitemap or connects to your CMS API, extracting titles, meta descriptions, URL slugs, and content summaries for each page.
Embeddings and indexing: I use Cloudflare Workers AI to generate vector embeddings for all content, then store them in Cloudflare Vectorize for fast semantic search capabilities.
Edge intelligence: A Cloudflare Worker intercepts 404 requests, parses the intended path, performs vector similarity search, and optionally applies custom reranking rules before returning structured suggestions.
Caching and configuration: Cloudflare KV stores ranking rules, domain-specific settings, and confidence thresholds. The Cache API ensures repeated lookups for popular phantom URLs stay lightning-fast.
Analytics integration: Every suggestion and click gets tagged with custom UTM parameters and sent to your analytics platform for detailed attribution tracking.
The typical flow works like this:
- Parse the phantom URL: Extract keywords from the 404 path, handle common transformations (hyphens to spaces, remove stop words)
- Vector search: Query Vectorize for the most semantically similar content on your domain
- Custom reranking: Apply business rules like boosting recent content, prioritizing high-converting pages, or filtering out deprecated sections
- Structured response: Return title, URL, snippet, and confidence score for each suggestion
- Performance optimization: Cache results by slug pattern to maintain edge performance
- Behavioral tracking: Log click-through rates and iterate on ranking algorithms
Content Ingestion Cloudflare Worker
// workers/content-ingestion.js
// Scheduled Worker to crawl content and generate embeddings
export default {
async scheduled(event, env, ctx) {
console.log('Starting content ingestion...');
try {
// Fetch sitemap and extract URLs
const urls = await this.fetchSitemapUrls(env.DOMAIN);
// Process URLs in batches to avoid rate limits
const batchSize = 10;
for (let i = 0; i < urls.length; i += batchSize) {
const batch = urls.slice(i, i + batchSize);
await Promise.all(batch.map(url => this.processUrl(url, env)));
// Small delay between batches
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
}
console.log(`Processed ${urls.length} URLs successfully`);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Content ingestion failed:', error);
}
},
async fetchSitemapUrls(domain) {
try {
const sitemapUrl = `https://${domain}/sitemap.xml`;
const response = await fetch(sitemapUrl);
const xmlText = await response.text();
// Basic XML parsing for URLs (you might want to use a proper XML parser)
const urlMatches = xmlText.match(/<loc>(.*?)<\/loc>/g);
if (!urlMatches) return [];
return urlMatches
.map(match => match.replace(/<\/?loc>/g, ''))
.filter(url => {
// Filter out non-content URLs
return !url.includes('/api/') &&
!url.includes('/admin/') &&
!url.includes('.pdf') &&
!url.includes('/tag/') &&
!url.includes('/category/');
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to fetch sitemap:', error);
return [];
}
},
async processUrl(url, env) {
try {
// Fetch page content
const content = await this.extractPageContent(url);
if (!content) return;
// Generate embedding using Cloudflare Workers AI
const embedding = await this.generateEmbedding(content.text, env);
// Prepare metadata
const metadata = {
url: url,
title: content.title,
snippet: content.snippet,
lastModified: new Date().toISOString(),
pageType: this.classifyPageType(url),
wordCount: content.text.split(' ').length
};
// Store in Vectorize
await env.VECTORIZE_INDEX.upsert([{
id: this.urlToId(url),
values: embedding,
metadata: metadata
}]);
// Cache content metadata in KV for fast access
await env.CONTENT_CACHE.put(
`content:${this.urlToId(url)}`,
JSON.stringify(metadata),
{ expirationTtl: 86400 * 7 } // 7 days
);
console.log(`Processed: ${url}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Failed to process ${url}:`, error);
}
},
async extractPageContent(url) {
try {
const response = await fetch(url, {
headers: {
'User-Agent': 'Content-Indexer/1.0'
}
});
if (!response.ok) return null;
const html = await response.text();
// Basic HTML parsing (consider using a proper HTML parser for production)
const titleMatch = html.match(/<title>(.*?)<\/title>/i);
const title = titleMatch ? titleMatch[1].trim() : '';
// Extract meta description
const descMatch = html.match(/<meta[^>]*name="description"[^>]*content="([^"]*)"[^>]*>/i);
const description = descMatch ? descMatch[1] : '';
// Extract main content (remove scripts, styles, nav, etc.)
let cleanText = html
.replace(/<script[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/script>/gi, '')
.replace(/<style[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/style>/gi, '')
.replace(/<nav[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/nav>/gi, '')
.replace(/<header[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/header>/gi, '')
.replace(/<footer[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/footer>/gi, '')
.replace(/<[^>]*>/g, ' ')
.replace(/\s+/g, ' ')
.trim();
// Limit text length for embedding
cleanText = cleanText.substring(0, 8000);
// Create snippet
const snippet = description || cleanText.substring(0, 160) + '...';
return {
title,
snippet,
text: `${title} ${description} ${cleanText}`.trim()
};
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Failed to extract content from ${url}:`, error);
return null;
}
},
async generateEmbedding(text, env) {
try {
const response = await env.AI.run('@cf/baai/bge-base-en-v1.5', {
text: [text]
});
return response.data[0];
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to generate embedding:', error);
throw error;
}
},
classifyPageType(url) {
if (url.includes('/blog/')) return 'blog';
if (url.includes('/docs/') || url.includes('/documentation/')) return 'docs';
if (url.includes('/product/') || url.includes('/features/')) return 'product';
if (url.includes('/case-study/') || url.includes('/customer/')) return 'case-study';
if (url.includes('/pricing/')) return 'pricing';
return 'general';
},
urlToId(url) {
return url.replace(/https?:\/\//, '').replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]/g, '_');
}
};404 Link Recovery Worker
// workers/link-recovery.js
// Main Worker to handle 404 requests and return suggestions
export default {
async fetch(request, env, ctx) {
// Handle CORS for API calls
if (request.method === 'OPTIONS') {
return this.handleCORS();
}
const url = new URL(request.url);
// Main recovery endpoint
if (url.pathname === '/api/recover-link') {
return this.handleLinkRecovery(request, env);
}
// Health check endpoint
if (url.pathname === '/health') {
return new Response('OK', { status: 200 });
}
return new Response('Not Found', { status: 404 });
},
async handleLinkRecovery(request, env) {
try {
const { pathname, domain } = await request.json();
if (!pathname || !domain) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({
error: 'Missing required parameters: pathname, domain'
}), {
status: 400,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
});
}
// Check cache first
const cacheKey = `suggestions:${domain}:${pathname}`;
const cached = await env.SUGGESTIONS_CACHE.get(cacheKey);
if (cached) {
console.log('Cache hit for:', pathname);
return new Response(cached, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'
}
});
}
// Generate suggestions
const suggestions = await this.generateSuggestions(pathname, domain, env);
// Cache results
const response = JSON.stringify({
suggestions,
cached: false,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
await env.SUGGESTIONS_CACHE.put(cacheKey, response, {
expirationTtl: 3600 // Cache for 1 hour
});
return new Response(response, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'
}
});
} catch (error) {
console.error('Link recovery failed:', error);
return new Response(JSON.stringify({
error: 'Internal server error',
suggestions: []
}), {
status: 500,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'
}
});
}
},
async generateSuggestions(pathname, domain, env) {
// Extract query terms from the pathname
const queryTerms = this.extractQueryTerms(pathname);
const queryText = queryTerms.join(' ');
console.log('Query terms:', queryTerms);
console.log('Query text:', queryText);
if (!queryText.trim()) {
return [];
}
try {
// Generate embedding for the query
const queryEmbedding = await env.AI.run('@cf/baai/bge-base-en-v1.5', {
text: [queryText]
});
// Search for similar content in Vectorize
const searchResults = await env.VECTORIZE_INDEX.query(queryEmbedding.data[0], {
topK: 10,
returnMetadata: true
});
console.log('Vector search results:', searchResults.count);
// Get configuration for ranking
const config = await this.getConfig(env);
// Rerank and filter results
const rankedSuggestions = await this.rankSuggestions(
searchResults.matches,
queryTerms,
config
);
// Return top suggestions with tracking parameters
return rankedSuggestions.slice(0, 4).map(suggestion => ({
title: suggestion.metadata.title,
url: this.addTrackingParams(suggestion.metadata.url, 'rag-404'),
snippet: suggestion.metadata.snippet,
score: suggestion.score,
pageType: suggestion.metadata.pageType
}));
} catch (error) {
console.error('Vector search failed:', error);
return [];
}
},
extractQueryTerms(pathname) {
// Remove leading/trailing slashes and split by common separators
const cleanPath = pathname.replace(/^\/+|\/+$/g, '');
// Split by slashes, hyphens, underscores
const segments = cleanPath.split(/[\/\-_]+/);
// Clean and filter terms
const terms = segments
.filter(segment => segment.length > 0)
.map(segment => {
// Remove common file extensions
return segment.replace(/\.(html|php|jsp|asp)$/, '');
})
.filter(term => {
// Filter out common web terms, numbers-only, very short terms
const stopWords = ['page', 'index', 'home', 'www', 'blog', 'post', 'article'];
return term.length > 2 &&
!stopWords.includes(term.toLowerCase()) &&
!/^\d+$/.test(term);
})
.map(term => {
// Convert camelCase and common abbreviations
return term
.replace(/([a-z])([A-Z])/g, '$1 $2')
.replace(/seo/gi, 'SEO')
.replace(/api/gi, 'API')
.replace(/cms/gi, 'CMS');
});
return terms;
},
async rankSuggestions(matches, queryTerms, config) {
const suggestions = await Promise.all(matches.map(async match => {
let score = match.score;
// Boost based on page type preferences
const pageType = match.metadata.pageType || 'general';
const typeBoost = config.pageTypeBoosts[pageType] || 1.0;
score *= typeBoost;
// Boost if query terms appear in title
const titleLower = (match.metadata.title || '').toLowerCase();
const titleMatches = queryTerms.filter(term =>
titleLower.includes(term.toLowerCase())
).length;
if (titleMatches > 0) {
score *= (1 + titleMatches * 0.2);
}
// Boost newer content
const lastModified = new Date(match.metadata.lastModified || 0);
const daysSinceModified = (Date.now() - lastModified.getTime()) / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24);
if (daysSinceModified < 30) {
score *= 1.1; // 10% boost for content modified in last 30 days
}
// Penalize very short content
const wordCount = match.metadata.wordCount || 0;
if (wordCount < 300) {
score *= 0.8;
}
return {
...match,
score: score
};
}));
// Sort by adjusted score
suggestions.sort((a, b) => b.score - a.score);
// Filter out low-confidence suggestions
return suggestions.filter(s => s.score > config.minConfidenceThreshold);
},
async getConfig(env) {
try {
const configJson = await env.CONFIG_KV.get('ranking_config');
const defaultConfig = {
pageTypeBoosts: {
'docs': 1.3,
'product': 1.2,
'blog': 1.0,
'case-study': 0.9,
'general': 0.8
},
minConfidenceThreshold: 0.7
};
return configJson ? { ...defaultConfig, ...JSON.parse(configJson) } : defaultConfig;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to load config:', error);
return {
pageTypeBoosts: {
'docs': 1.3,
'product': 1.2,
'blog': 1.0,
'case-study': 0.9,
'general': 0.8
},
minConfidenceThreshold: 0.7
};
}
},
addTrackingParams(url, source) {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
urlObj.searchParams.set('utm_source', source);
urlObj.searchParams.set('utm_medium', 'link-recovery');
urlObj.searchParams.set('utm_campaign', 'ai-hallucination-recovery');
return urlObj.toString();
},
handleCORS() {
return new Response(null, {
status: 200,
headers: {
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*',
'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'GET, POST, OPTIONS',
'Access-Control-Allow-Headers': 'Content-Type'
}
});
}
};🔑 Key Takeaway: I've found that combining semantic similarity with business logic (recency, page type, conversion history) typically improves click-through rates by 40-60% compared to pure search-based approaches.
The implementation requires several Cloudflare components:
- Scheduled Workers for content ingestion and embedding generation
- HTTP Workers for the 404 interception and suggestion logic
- Vectorize for fast similarity search across your content
- KV Storage for configuration and caching popular lookups
- Analytics Engine for detailed performance monitoring
Trade-offs to consider: This approach requires significant upfront engineering time. You'll need to build crawling logic, tune embedding models, and maintain ranking algorithms. But the payoff is a system that scales efficiently and gives you complete control over the user experience.
For context, I typically budget 2-3 weeks for the initial implementation, plus ongoing iteration as you learn from user behavior patterns.
Choosing Between Fix404.dev and Custom RAG
The decision usually comes down to time, resources, and control requirements.
Start with Fix404.dev if:
- You need to stop traffic bleeding this week
- Your development team is focused on core product features
- You want a proven solution that requires minimal maintenance
- Your content is well-organized and benefits from Google's understanding of your domain
Build custom Cloudflare RAG if:
- You need specific ranking logic that search engines can't provide
- You're managing multiple domains or complex content hierarchies
- Edge performance is critical for your user experience
- You want detailed control over suggestion algorithms and business rules
Most teams I work with follow a hybrid approach: implement Fix404.dev immediately to address the problem, then evaluate whether the recovered traffic justifies building a custom system. You can always layer additional intelligence on top of the quick fix.
Operational Playbook for Both Solutions
Regardless of which approach you choose, success depends on solid operational practices.
Governance and content management matter more than most teams realize. Maintain a canonical URL mapping to prevent duplicate content issues. When you retire or consolidate pages, update your suggestion systems to point toward the current authoritative version.
Quality guardrails prevent embarrassing suggestions. Set minimum confidence thresholds—never suggest pages that return 302 redirects or 404s themselves. I typically filter out very old content unless it's specifically evergreen material.
Experimentation drives improvement. A/B test suggestion placement, copy variations ("You might be looking for…" vs. "Related content"), and the number of suggestions displayed. I've found 3-4 suggestions typically outperform longer lists.
Reporting and iteration help you improve over time. Track weekly 404 volumes, recovered click rates, assisted conversions, and identify your most problematic phantom URLs. These patterns often reveal content gaps worth filling.
The key insight? Their most hallucinated URLs pointed to feature documentation that actually existed under different paths. This data guided their information architecture improvements and content cross-linking strategy.
Short story:
AI-generated content isn't going anywhere, and neither are the phantom URLs that come with it. But your 404 pages don't have to be dead ends anymore.
If you want immediate results with minimal engineering, add Fix404.dev to your 404 page today. You'll start recovering lost traffic within hours.
If you need sophisticated control and custom ranking logic, invest in building Cloudflare-powered RAG links. The upfront effort pays off through better user experiences and more qualified traffic recovery.
The bottom line? Google's John Mueller predicts we'll see a slight uptick of these hallucinated links being clicked over the next 6-12 months Google's Mueller Predicts Uptick Of Hallucinated Links: Redirect Or Not? before the problem stabilizes. That means you have a narrow window to implement solutions before this becomes table stakes for user experience.
Don't let phantom URLs drain your conversion funnel. Pick your approach, implement it this week, and start turning those frustrating 404s into recovered revenue.
The data is clear: hallucinated links are increasing, but the technology to recover that traffic is available today. The only question is whether you'll implement it before your competitors do.








