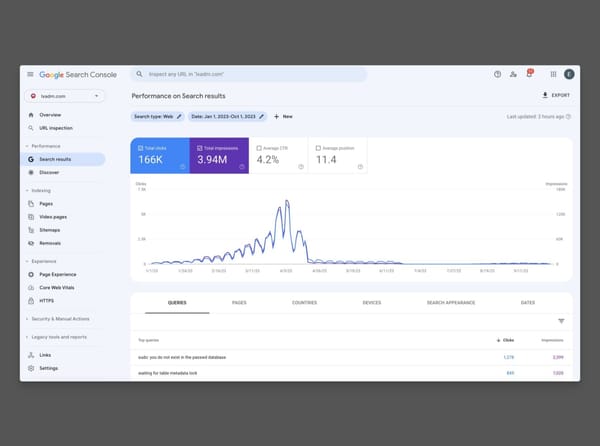
Throughout my entire career, I've placed great importance on reverse engineering and SEO experiments. The only way to understand the algorithm is to learn from the experiences of others and, of course, from the know-how gained from your own projects.
Let me give you some information about the education-only experiment I conducted on how CTR affects SERP ranking.
What is the purpose of this CTR experiment?
The aim of the CTR experiment is to see how CTR affects ranking by having bots that appear like real humans click on words with a search volume range of 100 to 200 that we have selected.
In short, I will have my websites, which rank 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th, and 8th on Google for certain words, periodically clicked on by bots with human-like artificial intelligence. The goal is to see a ranking increase after a certain period of time.
Technical challenges of the experiment and brief information on how we did it.
The Rand Fishkin example I gave below is a real-world example made over a tweet. In this experiment, I conducted the CTR experiment entirely through virtual browsers and IP addresses by virtual bots.
Challenges I encountered and overcame in this experiment:
Results of the CTR Manipulation Experiment
How our bots work 3 week for the daily schedule:
Using 20 different browsers and 20 different USA-based IP addresses, I targeted three keywords at different times of the day. I had the bots search for the keyword, click on the 1st position, spend time on the related website, show a tendency of not liking the content and click the back button, then visit my own website in the 7th position and spend time there.
Here is the result of the 3 keywords for 3 different website:
CTR Manipulation Experiment Website #1: The SERP position of the keyword we targeted on the first website started at 24th place, but after ten days, it settled at the 8th place. However, when we stopped the experiment, the ranking started to drop back down.
CTR Experiment Result Website #1
CTR Manipulation Experiment Website #2: On this website, we conducted an experiment that is actually not normal for Google. We had the bots click on the 1st result for the targeted keyword, then after returning to the SERP, visit our own website on the 2nd page. Despite this being a suspicious situation, we still obtained a positive result.
CTR Experiment Result Website #2
CTR Manipulation Experiment Website #3: I believe this website did not respond positively because the monthly search volume of the keyword I chose was quite low. I think we will get results when we conduct a longer test. Because I thought the impact of a keyword with no history in terms of CTR would be less.
I'm curious about your comments.
In the continuation of this blog post, I will be sharing information about general CTR.
Does CTR affect rankings? An old experiment from Rand Fishkin
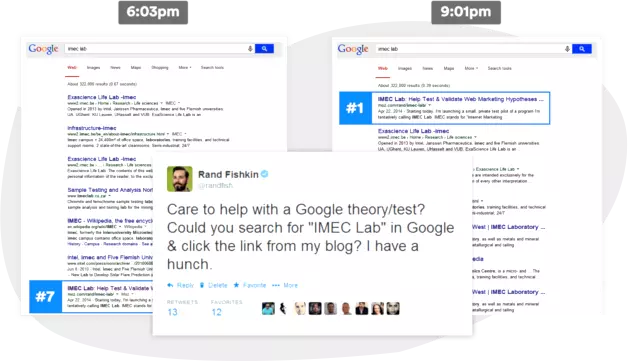
Rand Fishkin from Moz conducted a click-through rate (CTR) case study several years back. By directing clicks to his Google Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), he managed to elevate his site's ranking from #7 to #1 in under three hours.
The clicks were genuine, made by actual individuals. This study provided the initial evidence that CTR could significantly influence the positioning of SERPs.
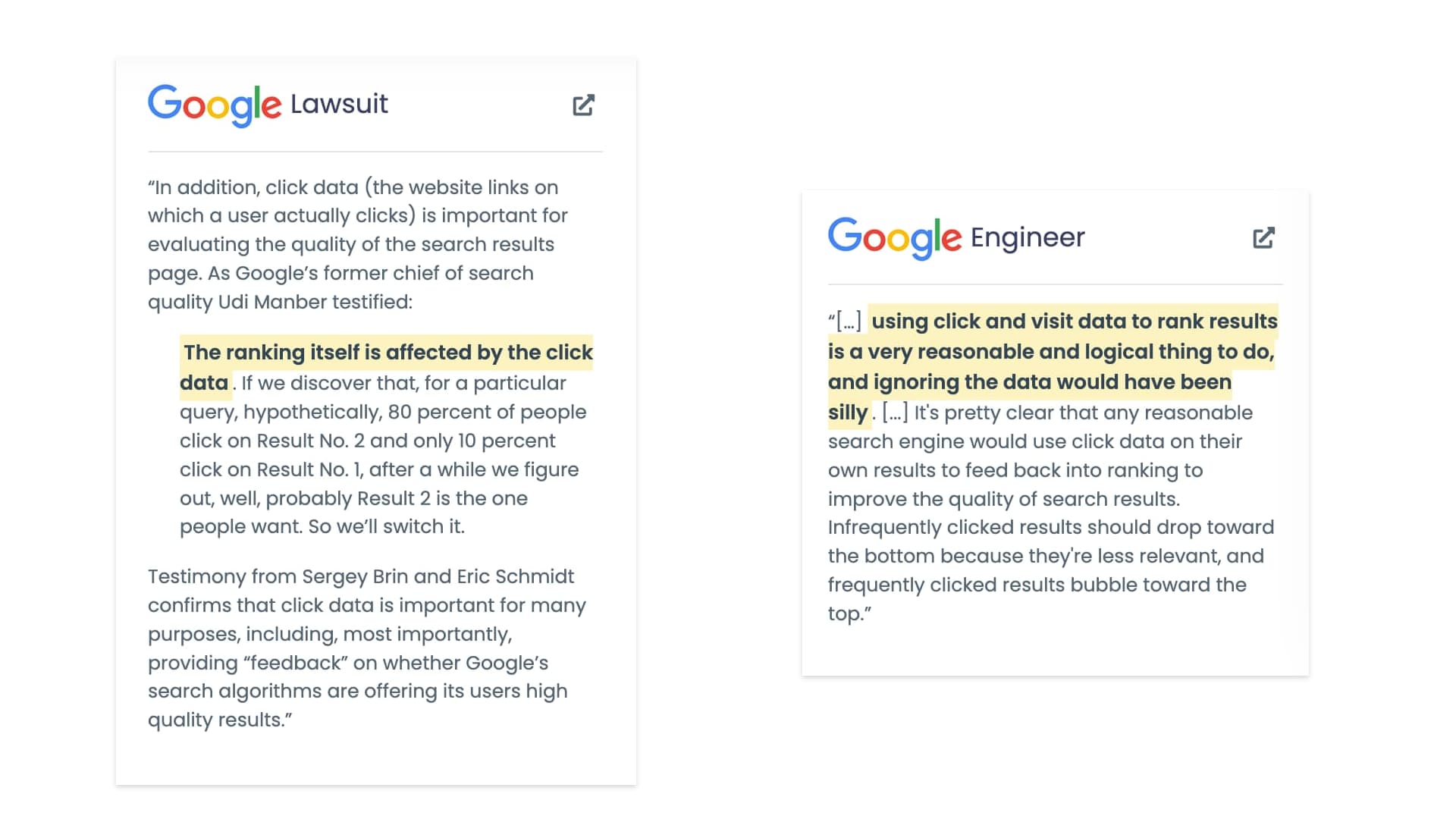
What does Google say about CTR?
On numerous occasions, Google has explicitly emphasized the significance of the click-through rate (CTR).

The #1 result in Google gets 49% of all clicks
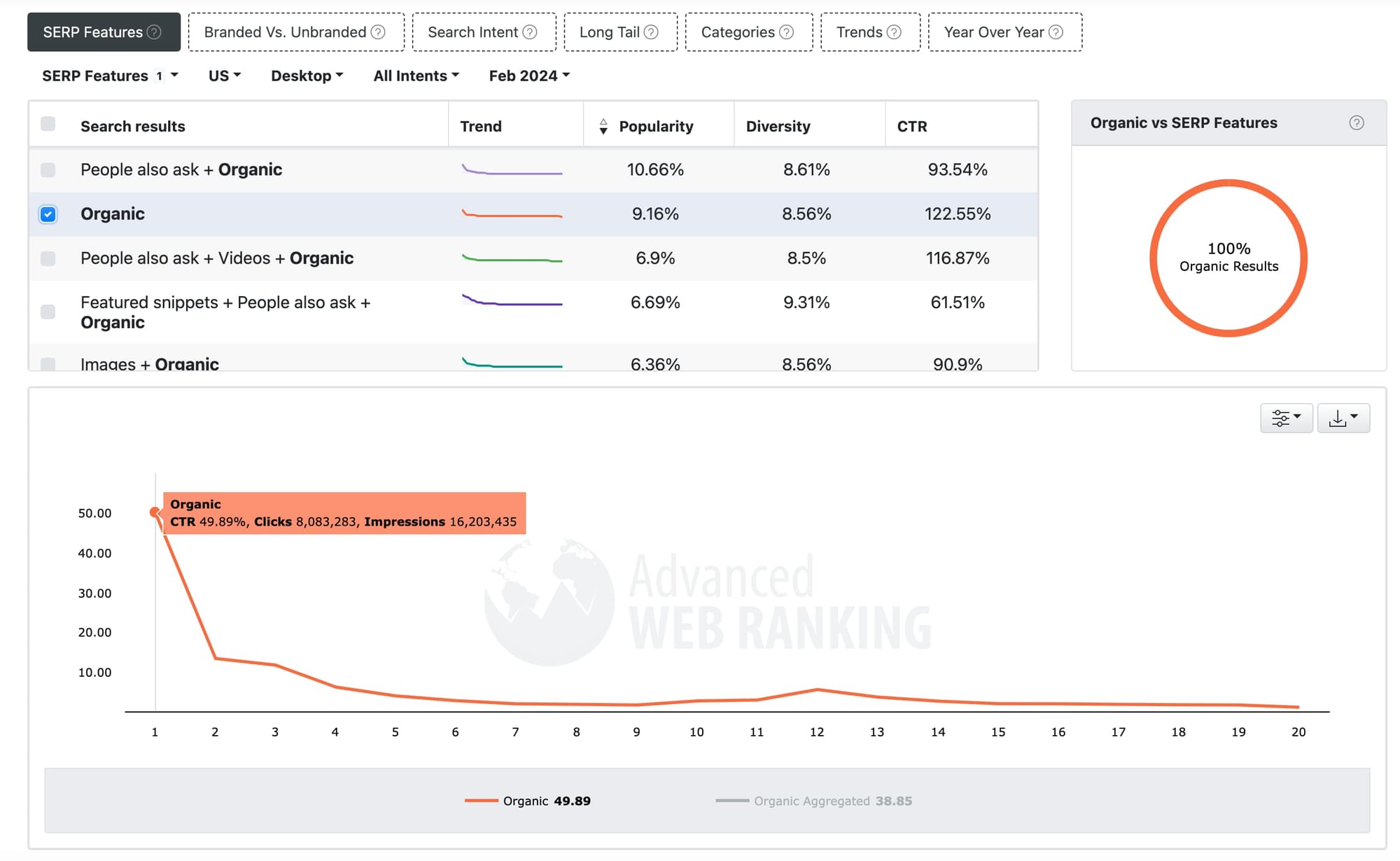
According to the CTR statistics shared for free by Advanced Web Ranking, the Google result in the 1st position receives 49% of clicks. Of course, CTR can vary depending on SERP features. In a SERP with Featured Snippets, People Also Ask, and organic results, the CTR for the 1st position is only 14%.
Here is my tips to increase CTR on Google SERP
- Identify your lowest organic CTR content to know where to start. Use Google Search Console for this.
- Fix any keyword cannibalization. Consolidate or differentiate the keywords you are trying to rank for.
- Get creative with your titles. Avoid heavy title tags, use brackets, try a numbered list, and always test your headlines.
- Use descriptive URLs. Optimize the slug when creating new pages.
- Optimize your description. Use emotional words and make sure your description is relevant.
- Utilize structured markup. This helps bring more visibility to your listing in the SERP.
- Leverage PPC Ads for Organic CTR. This allows you to quickly test different headlines and descriptions.
- Get emotional. Use emotional words in your titles or description.
- Use positive or negative sentiment. This has proven to drive higher CTR.
- Apply title case. This makes the heading stand out.
- Structure content for featured snippets. This can increase your CTR significantly.
- Improve page load time. A click only counts if the visitor actually lands on your website.
- Consider other engagement metrics. Look at bounce rate and make sure your content is valuable and easy to scan.
- Appeal to the searcher’s interest. Use power words and a call to action in titles.
- Write eye-catching titles. Use numbers, brackets, emoticons, and uppercase wisely.
- Optimize titles for search engines. Include your target keyword and make sure the title is between 45-60 characters.
- Optimize meta descriptions. Include your target keywords and do not exceed 160 characters.
- Apply structured data markup. This helps to form rich results in Google SERPs.
- Link pages properly to get sitelinks. Create a logical site structure and use descriptive anchor texts on internal links.
- Test your organic CTRs. Always test and recheck how your improvements perform.
Another comprehensive analysis of 5 million google searches: A study on Click-Through Rates by Backlinko
Backlinko analyzed 5 million Google search results to understand the dynamics of organic CTR and how it can be leveraged for better SEO results.
Companies are always striving to rank at the top of their target keywords. According to statistics from FirstPage, ranking on top of SERP in your niche generates a whopping 39.8% CTR rate in 2024. This is a massive traffic share, considering that the second and third-ranking results get 18.7% and 10.2%, respectively.
- The #1 result in Google’s organic search results has an average CTR of 27.6%.
- The #1 organic result is 10x more likely to receive a click compared to a page in the #10 spot.
- Organic CTR for positions 8-10 is virtually the same. Therefore moving up a few spots on the bottom of the first page may not result in more organic traffic.
- On average, moving up 1 spot in the search results will increase CTR by 2.8%. However, this depends on where you’re moving from and to. Moving from position #3 to position #2 will usually result in a significant CTR boost. However, moving from #10 to #9 doesn’t make a statistically significant difference.
- Titles that do and do not contain a question have similar CTRs.
- Title tags between 40 to 60 characters have the highest CTR. According to our data, pages with a title tag length between 40 and 60 characters have a TK% higher CTR compared to those that are outside of that range.
- Longer keywords tend to have a higher CTR: keywords between 10-15 words in length get 1.76x more clicks than single-word terms.
- URLs that contain terms similar to a keyword have a 45% higher click-through rate compared to URLs that don’t contain a keyword.
- Positive titles may improve your CTR. We found that titles with a positive sentiment improved CTR by approximately 4%.
By the end of the blog, we have gained a better understanding of the importance of CTR. I look forward to your comments and ideas for repeating the experiment in different cases.